Discover what is a CPU and how this essential component powers your computer. Our comprehensive guide explains the Central Processing Unit’s core functions, its crucial role in system performance, and why a CPU is the true brain behind every PC. Learn the secrets today!
This article explains what a CPU is, how it works, and why it is important for your computer. It also covers topics like CPU performance, temperature control, and the evolution from early computers to today’s multi-core processors.
What Is A Central Processing Unit (Cpu)?
A Central Processing Unit (CPU) is the principal component of a computer system, serving as its operational core. Often described as the “brain” of the computer, the CPU is indispensable for overall system performance.
It is responsible for executing the instructions of a computer program by performing a sequence of fundamental operations that include fetching, decoding, and executing commands. In technical terms, the CPU retrieves instructions from memory (fetching), interprets these instructions to determine the required actions (decoding), and then carries out these actions using its integrated circuits and control logic (executing).
This methodical cycle ensures that all computational tasks are processed efficiently and accurately, enabling the seamless operation of complex software applications and operating systems.
What Does Cpu Stand For?
The term “CPU” stands for “Central Processing Unit.” This designation reflects its role as the primary component responsible for executing the instructions that constitute a computer program.

In academic and technical contexts, the CPU is recognized as the central element in a computer’s architecture, facilitating the execution of operations that are fundamental to system performance and overall functionality.
What Does A Cpu Do?
A CPU (Central Processing Unit) executes instructions using the fetch-decode-execute cycle. It retrieves data from memory, decodes instructions to determine necessary actions, and executes them, ensuring smooth coordination among hardware components. This streamlined process is fundamental to system performance and overall computational efficiency, making the CPU the indispensable engine of modern computing.
What Is A CPU Usage?
CPU usage quantifies the proportion of processing power utilized by a computer’s Central Processing Unit (CPU) at any given moment. Expressed as a percentage, it represents the ratio of active processing cycles to the total available cycles over a specific time interval.
Elevated CPU usage typically indicates that multiple processes or resource-intensive tasks are concurrently operating, potentially leading to performance bottlenecks. Conversely, low CPU usage may suggest that the system is underutilized or that minimal background processing is occurring.
Monitoring CPU usage is essential for optimizing performance, managing workloads, and maintaining system stability, particularly in environments where computational resources are critically allocated.
What Is A Good Cpu Temp?
A good CPU temperature is defined as one that remains within the safe operational limits specified by the manufacturer. Under idle conditions, modern CPUs typically register temperatures between approximately 30°C and 50°C.
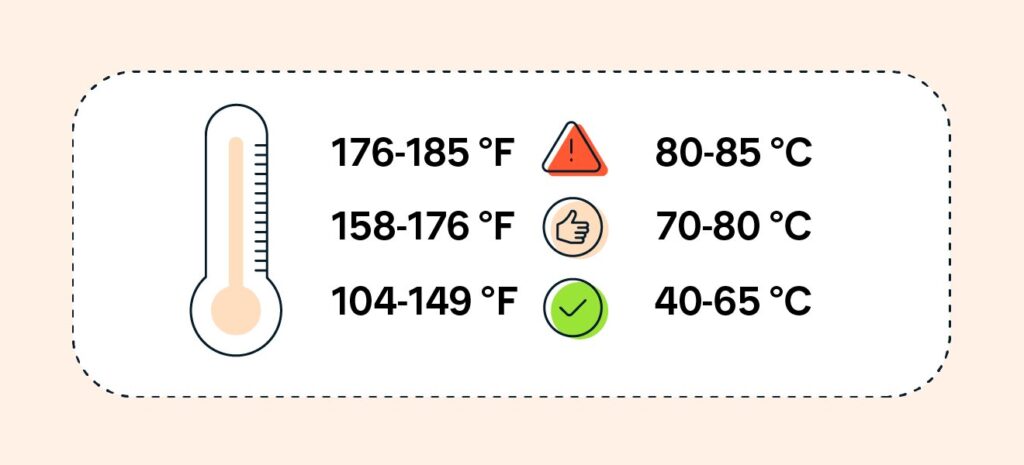
During intensive processing tasks, temperatures may rise to the range of 70°C to 85°C without adverse effects, although these values can vary depending on the specific model and cooling solutions employed.
It is imperative to adhere to manufacturer guidelines, as maintaining optimal thermal conditions is crucial for preventing thermal throttling, ensuring system stability, and prolonging the lifespan of the processor.
How to Check CPU Temp on Windows 10?
Windows 10 lacks a built-in CPU temperature monitor, necessitating the use of third-party applications. Tools such as Core Temp, HWMonitor, and SpeedFan provide real-time readings for each CPU core, enabling continuous monitoring under varying loads. Additionally, some manufacturers offer proprietary utilities with similar functions. Users should consult the tool’s documentation to accurately interpret the data and ensure optimal thermal management.
What Is The Architecture Of A Cpu?
The architecture of a CPU encompasses both its core hardware elements and the systematic process by which it operates. This design can be examined through two main lenses: the structural components and the operational cycle.
1. Core Components:
- Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU): The ALU is the computational heart of the CPU. It performs all mathematical computations and logical comparisons, enabling the processor to execute the fundamental operations required by software applications.
- Control Unit (CU): The CU orchestrates the execution of instructions by managing the flow of data between the CPU and other system components. It interprets program instructions and directs the ALU, registers, and other parts of the processor to perform specific tasks in a coordinated manner.
- Registers and Cache Memory: Registers provide the CPU with a small amount of high-speed storage for temporary data and instructions. Cache memory further enhances performance by reducing the time needed to access frequently used information, thereby speeding up overall data processing.
2. Operational Cycle:
The CPU processes instructions through a sequential cycle:
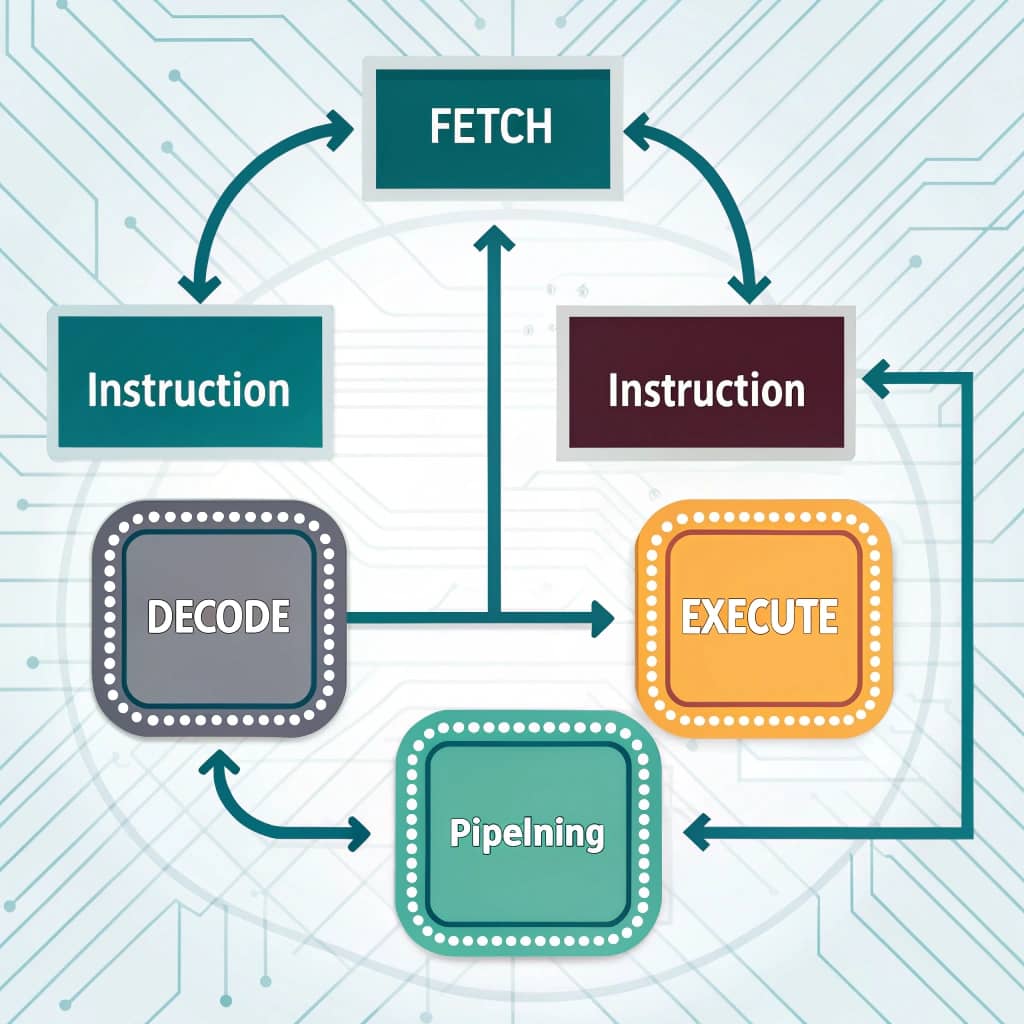
- Fetch: Retrieve the instruction from memory.
- Decode: Interpret the instruction to determine the required operation.
- Execute: Carry out the instruction using the ALU and other components.
- Instruction Pipelining and Parallelism: To maximize efficiency, modern CPUs utilize instruction pipelining, which breaks the fetch-decode-execute cycle into discrete stages. This allows multiple instructions to be processed concurrently. Parallelism further enhances performance by enabling the simultaneous execution of multiple instructions, thereby significantly increasing throughput.
This integrated architecture—combining robust hardware components with an efficient operational cycle—ensures that the CPU can manage complex computational tasks reliably and effectively, a necessity in contemporary computing environments.
Evolution of CPU Technology
The evolution of CPU technology reflects a remarkable journey from early, bulky computing machines to the sleek, high-performance processors of today. This progression is marked by significant technological breakthroughs that have transformed the way computers operate.
1. Historical Development
Early computing machines were constructed using technologies such as vacuum tubes and mechanical relays. While these devices were foundational in the development of electronic computing, they were limited by their large size, high power consumption, and frequent reliability issues.
2. Transition from Vacuum Tubes to Transistors
A major turning point occurred with the introduction of transistors. Transistors replaced vacuum tubes because they were smaller, more energy-efficient, and offered greater reliability. This transition addressed many of the deficiencies inherent in earlier designs, enabling more compact and robust computing systems.
3. Rise of Microprocessors
The next pivotal advancement was the development of microprocessors. By integrating all the core functions of a CPU onto a single silicon chip, microprocessors revolutionized the computing landscape. This integration led to significant improvements in processing power, reduced costs, and a decrease in physical size, which in turn spurred the widespread adoption of personal computers and a broad range of digital devices.
How Many Types Of Cpus Are There?
In the context of computer CPUs, the number of cores is a critical indicator of performance, particularly in terms of multitasking and parallel processing capabilities. The evolution of multi-core processors has led to a range of configurations, each offering distinct advantages for various applications:
- Single-core Processors: Traditionally, these processors contain one processing unit. While they were predominant in early computing systems, they are now largely supplanted by multi-core designs due to limitations in handling multiple simultaneous tasks.
- Dual-core Processors: Featuring two cores, dual-core CPUs enhance performance by allowing parallel execution of processes. This configuration is particularly beneficial for general multitasking and light to moderate computing tasks.
- Quad-core Processors: With four independent cores, provide a significant performance boost over dual-core systems. They are widely adopted in consumer devices, offering a balanced mix of speed and efficiency for both everyday computing and moderately demanding applications.
- Hexa-core Processors: Incorporating six cores, hexa-core CPUs are well-suited for high-end consumer and professional applications. They deliver improved performance in multi-threaded environments, making them ideal for tasks that require substantial computational power.
- Octa-core Processors: With eight cores, octa-core processors offer robust parallel processing capabilities. This configuration is advantageous for intensive computing tasks such as gaming, video editing, and complex simulations, where the ability to handle multiple threads concurrently is critical.
- Deca-core Processors: Which integrate ten cores, represent the forefront of mainstream consumer CPU technology. They provide exceptional performance for highly demanding applications, ensuring efficient processing in environments that require maximum throughput.
Each of these configurations addresses specific computational requirements, illustrating the industry’s continuous efforts to enhance processing power and efficiency through multi-core technology.
What Is Cpu Performance?
CPU performance is a multifaceted measure of how effectively a central processing unit executes instructions and processes data. It is influenced by several critical factors:
1. Clock Speed and Core Count:
The clock speed, expressed in gigahertz (GHz), determines the number of cycles a CPU can complete per second, thereby directly impacting its ability to process instructions. Equally important is the core count; multiple cores enable a CPU to execute parallel tasks, enhancing multitasking and overall computational throughput.
2. Thermal Management and Overclocking:
Effective thermal management is essential to sustain optimal performance. Adequate cooling prevents overheating, which can lead to thermal throttling—a protective mechanism that reduces clock speeds to avoid damage. Overclocking, the process of increasing a CPU’s operating frequency beyond its rated specification, can further boost performance; however, it necessitates careful thermal management to mitigate risks such as reduced component lifespan and stability issues.
3. Cache and Memory Hierarchy:
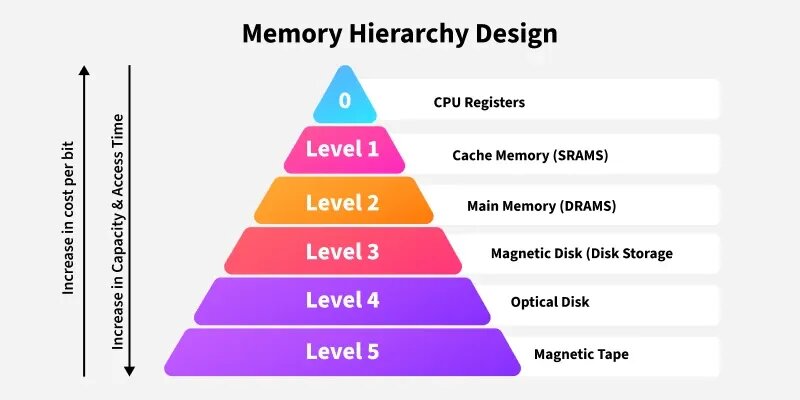
The cache serves as a high-speed repository for frequently accessed data, significantly reducing latency and accelerating processing times. An optimized memory hierarchy, often comprising multiple cache levels, ensures that the CPU can quickly retrieve and process data, thereby minimizing performance bottlenecks.
FAQ’s
1. What Is The Primary Role Of A Cpu?
The primary role of a CPU is to execute program instructions and manage data processing, thereby coordinating the activities of all computer components to ensure seamless system functionality.
2. How Does The Cpu’s Clock Speed Affect Performance?
The CPU’s clock speed, measured in gigahertz (GHz), determines the number of cycles available for executing instructions, thereby directly influencing processing efficiency. Higher clock speeds generally result in faster computation, although overall performance is also affected by the processor’s architecture and core count.
3. What Are The Differences Between Single-Core And Multi-Core Processors?
Single-core processors contain a single processing unit that executes tasks sequentially, whereas multi-core processors integrate multiple cores to concurrently process several instruction streams, enhancing multitasking and overall computational efficiency.
4. How Can Overclocking Improve Cpu Performance, And What Are Its Risks?
Overclocking enhances CPU performance by increasing its clock speed beyond specified limits, thereby accelerating instruction execution. However, this practice may lead to increased thermal output, potential system instability, and a reduced lifespan of the processor if not properly managed.
5. What Are The Emerging Trends In Cpu Technology?
Emerging trends in CPU technology include the integration of AI accelerators, enhanced energy efficiency, and the development of heterogeneous architectures that combine various processing units to optimize performance.
Conclusion:
The CPU is the indispensable engine of modern computing, acting as the central unit that processes instructions and manages data flow. Its performance is determined by factors such as clock speed, core count, and thermal management, which together ensure efficient operation. The evolution from early vacuum tubes to advanced microprocessors highlights continuous innovation and improved efficiency. Understanding CPU architecture and performance is essential for optimizing system functionality and supporting the demands of today’s technology.